Signature Collection
Explore SignatureUAE mortgage laws are designed to protect consumers by ensuring transparency and fairness in the lending process. These laws require lenders to provide clear and comprehensive information about loan terms, interest rates, fees, and any associated risks. The transparency allows borrowers to make informed decisions when selecting a mortgage.
Securing a mortgage in the UAE requires understanding the distinct legal frameworks across the Emirates. While property mortgages are governed by federal law, the specifics can vary by region. If you prefer buying a home with a mortgage instead of cash, our ultimate guide provides all the essential information. Learn everything about UAE mortgage regulations before starting your application process.
Key Components of UAE Mortgage Laws
We are here to help you navigate UAE mortgage regulations. At Provident, our mortgage experts offer comprehensive guidance to homebuyers and investors on UAE mortgage legalities. Let’s explore the key components of the legal framework surrounding mortgage loans.

Mortgage Registration
Dubai has a well-developed property registration system that requires all real estate interests, including mortgages, to be registered with the Dubai Land Department (DLD). Mortgages in Dubai can be registered over freehold, leasehold interests, and even off-plan properties.
A mortgage becomes effective against third parties upon registration in the land register of the respective emirate. The UAE Civil Code mandates that a valid mortgage requires proper registration and payment of fees. Priority is determined by the first-to-record principle, meaning the first registered mortgage has precedence over others. A mortgage over land includes all fixtures and buildings attached to it.
Dubai’s property registration system is governed by the Dubai Property Registration Law (Law No. 7 of 2006) and the Dubai Mortgage Law (Law No. 14 of 2008). Mortgages in Dubai must be registered with the DLD, covering both conventional and Shariah-compliant (Ijara) financing. The DLD provides a standard mortgage agreement form, which must be signed by all parties in the presence of DLD officials. Although Islamic lenders are listed as owners, they must follow the same legal enforcement procedures as conventional lenders.
Central Bank UAE Mortgage Regulations
The Central Bank of the UAE establishes the Dubai mortgage borrowing guidelines. These regulations apply to banks, finance companies, and other financial institutions providing mortgage loans. As per the bank, the borrower needs to consider these factors before applying for a mortgage in the UAE:
- Income Limitation: Typically, your mortgage is capped at 7 times your annual salary.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): Your total monthly debt, including your future mortgage, should not exceed 50% of your salary.
- Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio UAE: The maximum LTV is 80% for expats and 85% for Emiratis, with lower LTVs for off-plan properties.
- Loan Term: The maximum loan term is 25 years, up to retirement age.
- Property Valuation: The loan amount is based on the lower of the purchase price or the official valuation.
- Stress Test: Lenders assess your ability to manage payments even if interest rates rise, aiming to keep mortgage payments within 50% of your monthly income.
UAE Mortgage Eligibility
Mortgage eligibility in the UAE depends on factors like income, employment status, credit history, and the type of property. Lenders typically require a minimum monthly income, employment stability, and a good credit score. Foreign buyers can obtain a mortgage in the UAE, but specific criteria must be met. Typically, you need to have been in your current job for at least six months to a year, depending on the location and lender's policies.
Self-employed individuals must have been operating their businesses for at least two years. Having an existing relationship with the bank can be advantageous. However, some banks only accept applicants working for certain companies, so those with smaller employers may face difficulties. Moreover, a clean credit history is crucial, as lenders may reject applicants with poor or nonexistent credit records. If you're new to credit, consider building a history with a credit card.
Types of Mortgages
There are various types of mortgages available in the UAE. Here is the list:
- Fixed-Rate Mortgage: The interest rate is set at the beginning of the loan and remains unchanged for a specific period, typically less than five years.
- Variable-Rate Mortgage: The interest rate fluctuates based on market conditions throughout the loan term.
- Remortgage: A remortgage allows you to replace an existing mortgage with a new one, either with the same lender or a different one. This option is often chosen to secure a lower interest rate or extend the payment period.
- Offset Mortgage: This type links your mortgage with deposit accounts, reducing interest payments based on your account balances. Though the interest rate is higher, it offers flexible repayment options.
- Investment Mortgage: This mortgage is used to finance property for rental or resale and applies to properties with up to four units. Larger properties fall under different regulations.
- Non-Resident Mortgage: These mortgages are available to non-UAE residents and typically cover up to 50% of the property’s value with higher monthly payments and shorter terms. As per expatriate mortgage rules in the UAE, the eligibility criteria for non-resident mortgages include being from an approved country and meeting income requirements.
Special Mortgage Types
Off-Plan Property Mortgages:
Off-plan property mortgages are designed for properties that are still under construction. These mortgages typically have stricter terms, such as lower Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratios, often around 50%. The financing is usually tied to the development's progress, and lenders may have specific requirements based on the project’s stage and the developer's reputation.
Shari’ah-Compliant Mortgages:
Shari’ah-compliant mortgages, also known as Islamic mortgages, adhere to Islamic principles, prohibiting interest (riba). Instead, they use structures like Ijara (leasing) or Murabaha (cost-plus financing), where the bank buys the property and then leases or sells it to the borrower at a profit. These mortgages are structured to align with Shari’ah law, offering an alternative to conventional mortgage products for Muslim borrowers.
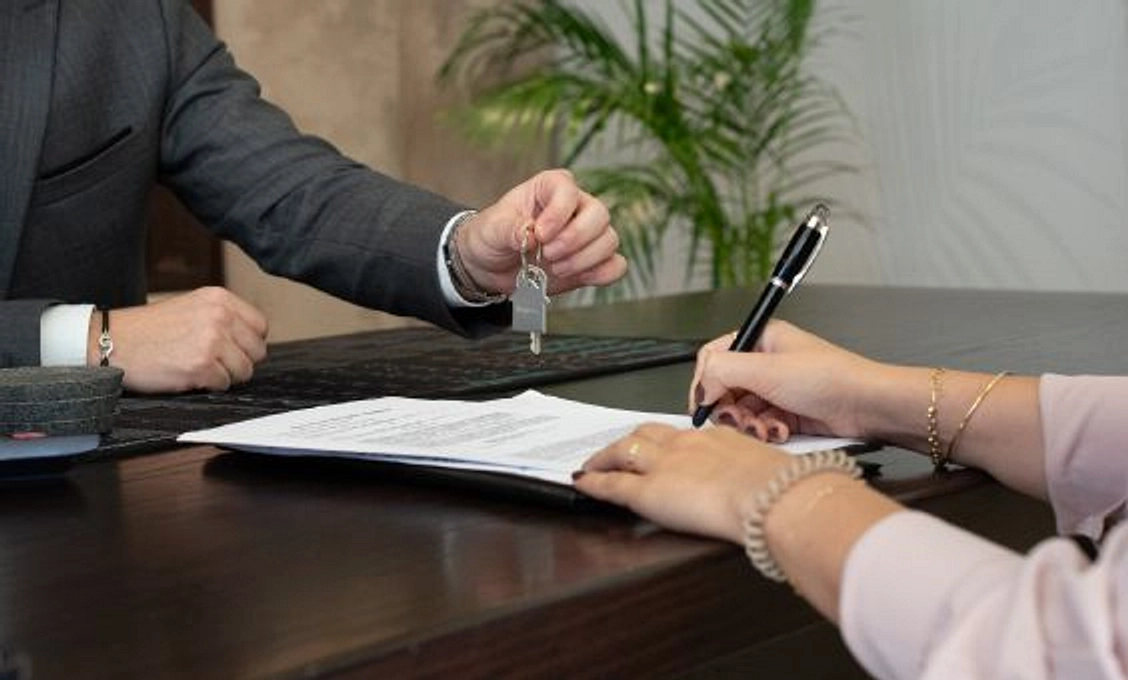
Application Process
The mortgage loan process in the UAE typically involves pre-approval, property selection, application submission, and final approval. It starts with getting pre-approved by a lender, determining how much you can borrow. After selecting a property, you submit a formal mortgage application, followed by the lender’s evaluation, and if approved, the loan is disbursed.
Documentation Requirements
When applying for a mortgage, the required documents may differ depending on the bank. However, lenders typically request the following:
- A copy of your passport and/or Emirates ID
- Borrower identification (residents might need to provide proof of residence in the UAE)
- Detailed requirements for property documents
- Financial documents, such as proof of income, bank statements, or your tax return
For more information, get in touch with us at Provident
 Apartments
Apartments Villas
Villas Townhouses
Townhouses Penthouses
Penthouses Commercial
Commercial See All Properties
See All Properties Commercial
Commercial Property Management
Property Management List Your Property
List Your Property Mortgages
Mortgages Conveyancing
Conveyancing Short Term Rentals
Short Term Rentals Property Snagging
Property Snagging Partner Program
Partner Program Currency Exchange
Currency Exchange PRYPCO
PRYPCO Ethnovate
Ethnovate Plots
Plots
